Windows Core Processes
Windows core processes are fundamental components of the operating system that manage various essential functions to keep computer running smoothly. These processes handle everything from starting up system to managing hardware and software operations. Here’s a brief overview of some key core processes in Windows and how you can detect anomalies within them:
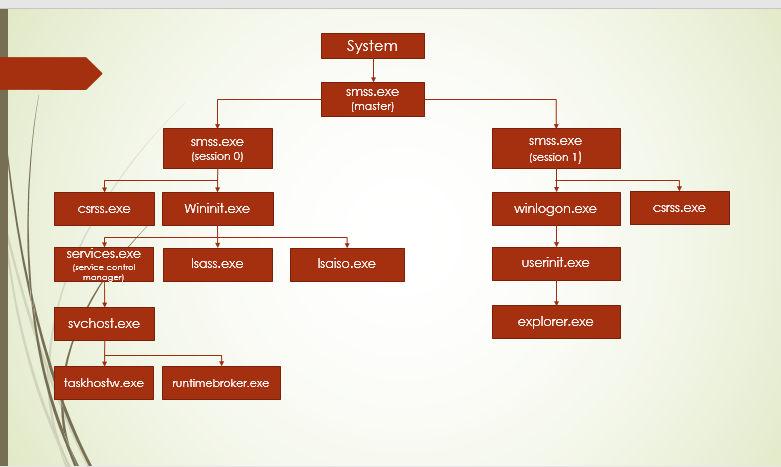 Image source: dfir-world.tumblr.com
Image source: dfir-world.tumblr.com
SYSTEM
The SYSTEM process is the very first process that runs when Windows starts, often referred to as the System Idle Process. It plays a crucial role in managing low-level operations and system resources, ensuring everything functions smoothly behind the scenes. The SYSTEM process takes care of tasks like running core system threads, handling hardware interrupts, and overseeing essential services. It always has a Process ID (PID) of 4 and operates without a parent process, running under the NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM user account.
Normal Behavior:
- PID: Always 4
- Parent Process: None
- User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Start Time: At system boot
- Number of Instances: Only one instance after boot
Abnormal Behavior:
- PID: Anything other than 4
- Parent Process: Presence of a parent process (which shouldn’t exist)
- Command-Line Arguments: The process should not have any
- Multiple Instances: More than one instance of the SYSTEM process running
smss.exe (Session Manager Subsystem)
smss.exe, also known as the Session Manager Subsystem, is a crucial process in Windows. It manages the creation of new sessions and the setup of environment variables. The parent process for smss.exe, often referred to as the master smss.exe, is the SYSTEM process.
When smss.exe runs, it creates two sessions:
- Session 0: Responsible for creating
csrss.exeandwininit.exe. Both of these processes are isolated sessions of the OS. - Session 1: Responsible for creating
csrss.exeandwinlogon.exe.
After these tasks are completed, the child instances of smss.exe will exit, leaving only the master process active.
Normal Behavior
- User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: SYSTEM
- Instances: Only one instance after boot-up
- Path:
%systemroot%\System32\smss.exe - Command-Line Arguments: None
Abnormal Behavior
- Parent Process: Anything other than SYSTEM, or if the parent process has a PID other than 4
- Command-Line Arguments: Presence of command-line arguments
- Start Time: Should be a few seconds after SYSTEM
- User Account: Anything other than
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
CSRSS.exe (Client/Server Runtime Subsystem)
csrss.exe, or Client/Server Runtime Subsystem, is a vital Windows process responsible for the creation and management of Windows consoles and threads. It plays a crucial role in authentication, authorization, and enforcing security policies within the operating system.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\csrss.exe - Number of Instances: Two or more
- User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Not visible, as
smss.exewill exit after spawningcsrss.exe
Abnormal Behavior
- Parent Process: Any process other than
smss.exe - Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\csrss.exe
WININIT.EXE
Wininit.exe is a crucial system process in Windows, standing for Windows Initialization. It handles the startup of key system components by reading and executing commands from the winInit.ini file. Essentially, it plays a significant role in initializing essential parts of the operating system.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\wininit.exe - User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Not visible, as
smss.exewill exit after spawningcsrss.exe. - Number of Instances: One
- Command-Line Arguments: None
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\wininit.exe - User Account: Any account other than
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Visible parent processes or unusual parent-child relationships
- Number of Instances: More than one
- Command-Line Arguments: Presence of command-line arguments
SERVICES.EXE
As name says Services.exe is responsible for managing system services. These services run in the background and are essential for various Windows functions, such as managing network connections, ensuring security, handling device drivers, and more.
### Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\services.exe - User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Wininit.exe
- Number of Instances: One
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\services.exe - User Account: Any account other than
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Parent processes other than
wininit.exe. - Number of Instances: More than one instance running simultaneously
Lsass.exe
The Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (lsass.exe) handles user authentication by using packages specified in the HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa registry key. It also creates security tokens for SAM (Security Account Manager), AD (Active Directory), and NETLOGON. Because it deals with sensitive authentication data, this process is often targeted by malware. Tools like mimikatz can exploit it to read this registry key and steal credentials.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\lsass.exe - User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process:
wininit.exe - Number of Instances: Only one; should not have any child processes except for EFS (Encrypting File System).
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\lsass.exe - User Account: Any account other than
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Parent processes other than
Wininit.exe
LSAiso.exe
LSAiso.exe (or LSA Isolated) is a legitimate Windows process that runs in Virtual Secure Mode (VSM) as an Isolated User Mode (IUM) process. You will only see LSAiso.exe if Credential Guard is enabled.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\lsaiso.exe - User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process:
wininit.exe - Number of Instances: Only one
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\lsaiso.exe - User Account: Any account other than
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Parent processes other than
wininit.exe - Other: Presence of the process when Credential Guard is disabled
svchost.exe
svchost.exe serves as a host process for loading services from DLL files. Due to the numerous services required for Windows to function properly, multiple instances of svchost.exe typically run simultaneously. Because of this, malware often attempts to blend itself by using similar names, such as scvhost.exe, which can be difficult for an unexperienced eye to spot.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\svchost.exe - User Account: Varies; some instances run as the logged-in user
- Parent Process:
services.exe - Command-Line Arguments: must contain ‘-k’ parameter
- Number of Instances: Many
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\svchost.exe - User Account: Unusual user accounts, especially those not typically associated with service processes
- Parent Process: Parent processes other than
services.exe
RuntimeBroker.exe
This process is responsible for managing and verifying permissions required by other processes, such as access to the microphone, location, and other system features.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\runtimebroker.exe - User Account: Same as the logged-on user
- Parent Process:
svchost.exe - Number of Instances: Only one
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\runtimebroker.exe - User Account: Any account other than the logged-on user
- Parent Process: Parent processes other than
svchost.exe - Number of Instances: More than one instance running simultaneously
TASKHOSTW.exe
Taskhostw.exe is a Windows process that hosts DLL files related to scheduled tasks. Its name may vary across different versions of Windows, as Microsoft has changed it multiple times. you can often identify the version of Windows by the name of this process.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\taskhostw.exe - User Account: System or the same as the logged-on user
- Parent Process:
svchost.exe - Number of Instances: Multiple instances can be seen
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\taskhostw.exe - Parent Process: Parent processes other than
svchost.exeor having no parent process
LSM.EXE
Local Session Manager (LSM) is responsible for managing user sessions, including creating and deleting them. It ensures that sessions are kept isolated from each other and handles requests to smss.exe to start new sessions. In Windows 10, it is seen as a service DLL named lsm.dll.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\lsm.dll(In Windows 10, it is seen as a service DLL) - User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process:
wininit.exe - Number of Instances: Only one
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\lsm.dll(In Windows 10, it should appear as a service DLL) - User Account: Any account other than
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Parent processes other than
wininit.exe - Number of Instances: More than one instance running simultaneously
WINLOGON.exe
winlogon.exe handles user logons and logoffs. When a user logs in, winlogon.exe is responsible for loading the user profile into the registry under HKEY_CURRENT_USER.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\System32\winlogon.exe - User Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process:
smss.exe - Number of Instances: Varies based on the number of logged-on users
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\System32\winlogon.exe - User Account: Any account other than
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM - Parent Process: Parent processes other than
smss.exe - Number of Instances: Unusual number of instances, such as multiple instances when only one is expected
Explorer.exe
explorer.exe is the process that provides users with access to their files and folders and offers the graphical interface for interacting with Windows. It handles the desktop environment, taskbar, and file management functions.
Normal Behavior
- Image Path:
%SystemRoot%\explorer.exe - User Account: Same as the logged-on user
- Parent Process:
wininit.exe - Number of Instances: Typically one per user session
Abnormal Behavior
- Image Path: Any path other than
%SystemRoot%\explorer.exe - Parent Process: Parent processes other than
wininit.exe
References
- DFIR World: Windows 10 Core Processes
- 0xcybery: Core Processes In Windows System
- MalwareTips: Local Session Manager Process - What You Need to Know
- How-To Geek: What is Windows Logon Application (winlogon.exe) and Why is it Running on My PC?
- The Windows Club: What is Taskhostw.exe
- Help Desk Geek: What is Lsaiso.exe and How to Reduce Its High CPU Usage
- MalwareTips: Wininit.exe - What It Is & Should I Remove It?